Owning a public company and being a founder at a startup are two different ball parks.
Not just in terms of revenue, size, licenses, shareholders, taxes, LLCs, location, and people, there’s something deeper that both focus on at different scales. If you want to learn if a company or startup is the best career choice, I suggest you read here.
The main focus for any size or profitable/unprofitable company is that they need funding in order to invest in a project.
That’s where alternative investments come into play.
You usually do need money to make money.
Public companies have it easier. They can turn to financial markets to issue types of debt and equity securities but when entrepreneurs need money to start a business, they aren’t able to issue debt or equity securities to the public yet so they will seek out loans from banks, although the amount of money they can borrow is often limited.
What’s strange is that banks will lend every day people loans who can’t afford them and not remind them their credit card balance is overdue, but they will not finance new and young companies because the risk of not getting their money back is too high.
This leads companies to tap into alternative investment strategies that have the opportunity to take on risk for massive gain because high risk = high reward.

My Journey
Funding is a tough crucial part of business. As someone who just sold my startup, it is far the hardest kickstarter even though they always say and by ‘they’ I have no clue, “if you have a great idea, finding the money to support it is easy.”
Not necessarily because first off, the idea isn’t what usually matters, it’s the founder and second, just like recruiting, getting to know investors is a full-time job.
Getting into bootcamps and accelerators ranging from YC to Founder’s Fund is notoriously competitive, harder than Harvard which ironically most founders that did go through the entrepreneurial program flunked out of that school.
Investors, VCs and Angels are looking for out of the box thinkers, not event the idea because the idea has to be boring and simple, otherwise no one would benefit from it.
They want to get to know the team because behind any brand is the leader. To test if they’re a true leader, see how they’ll do with a cash burn rate of up to 10 years. If they can withstand that with patience and grit till then, they’ll make it anywhere.
Most ideas aren’t really unique, its the strategy behind it.
Young companies and entrepreneurs turn to their first safest bet: venture capitalists who specialize in financing these folks. They provide the capital and expertise to launch and grow their business. This was the only way I could find funding after trying multiple sources. A private equity firm found me through a road show pitching contest by chance. The most unexpected events usually lead to the best outcomes.

Alternative Investments
#1 Private Equity
These are firms that invest in private companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange. Although people commonly refer to private “equity”, these investments include both equity and debt securities. Debt investments, however, are less common than equity investments.
Private equity is often categorised according to the stage of development of the companies it invests in.
Categories include venture capital, growth equity, buyouts, and distressed investing as illustrated below:
Venture Capital (riskiest type): Many companies fail than succeed. This is a form of private equity to help fund those prospects at the beginning stages, which is itself a type of alternative investment.
Growth Equity: This is a private equity investment strategy that usually focuses on financing companies with proven business models, good customer bases and positive cash flows and or profits.
These companies have an opportunity to grow but they do not generate sufficient cash flows from their operations to support their growth plans so they provide additional money in return for equity. Some also help companies prepare for an initial public offering(IPO) to take a company public.
Buyouts: The financing of the transaction involves a high proportion of debt are often called leveraged buyouts (LBOs).
Distressed: When companies encounter financial troubles, they may be at risk of not being able to make full and timely payments of interest and/or principal.

#2 Real Estate
Direct or indirect investments in land and buildings
Additional Types of Real Estate:
Land
Offices
Commerical Real Estate
Crowd Fuding
Multifamily Reisdential Dwellings
Reatil Properties
Hotels
REITS-like equity securities, shares of REITS are traded on exchanges, more liquid than real estate
Investors can buy real estate directly or gain exposure to real estate through the private market via real estate limited partnerships and real estate equity funds, or through the public market via real estate investment trusts.

#3 Commodities
Your most precious commodities are your time and attention becuase you cannot buy them back.
These are investments in physical products, such as precious and base metals (e.g., gold, copper), energy products (e.g., oil), and agricultural products that are typically consumed (e.g., corn, cattle, wheat) or used in the manufacture of goods (e.g., lumber, cotton, sugar)
Purchase of commodity derivatives. As mentioned in the Derivatives section, investors can buy derivatives in which the underlying asset is a commodity or a commodity index. Typical commodity derivatives are forwards, futures, options, and swaps.
Futures and some types of options are traded on exchanges, whereas forwards, swaps, and other types of options are privately negotiated agreements.
To gain exposure to commodities, investors can buy the physical commodity, shares of natural resources or commodity-related companies, or commodity derivatives.

Recap
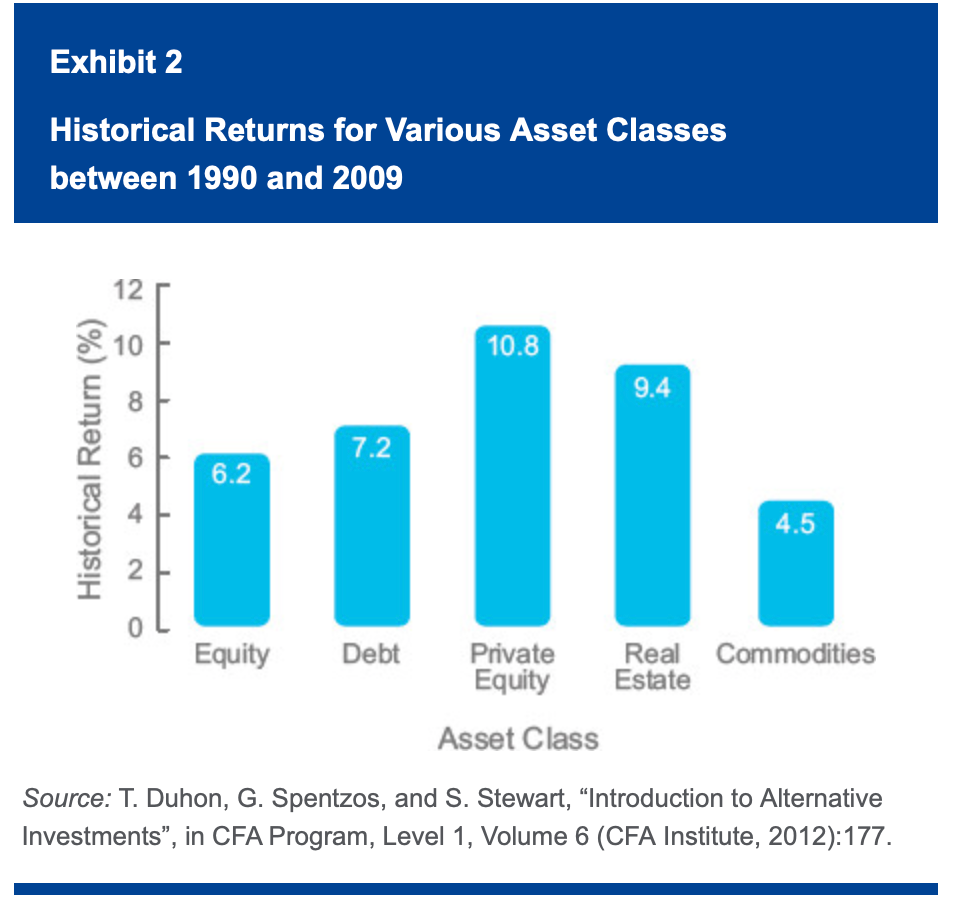
Private equity, real estate, and commodities are all considered alternative because they represent an alternative to investing exclusively in “traditional” asset classes, such as debt and equity securities.
When it comes to timing, real estate and commodities are among the oldest types of investments.
Differentiators +Advantages
These alternative investments look completely unrelated to each other which is a good thing. They should make your portfolio as diverse as possible. But they do have common advantages that enhance returns and reduce risk.
2 Main Reasons to Invest:
-Enhance returns
-Reduce risk by obtaining diversification benefits
They also share similar limitations: typically, they are less regulated, transparent, liquid, and easier to value than debt and equity investments.
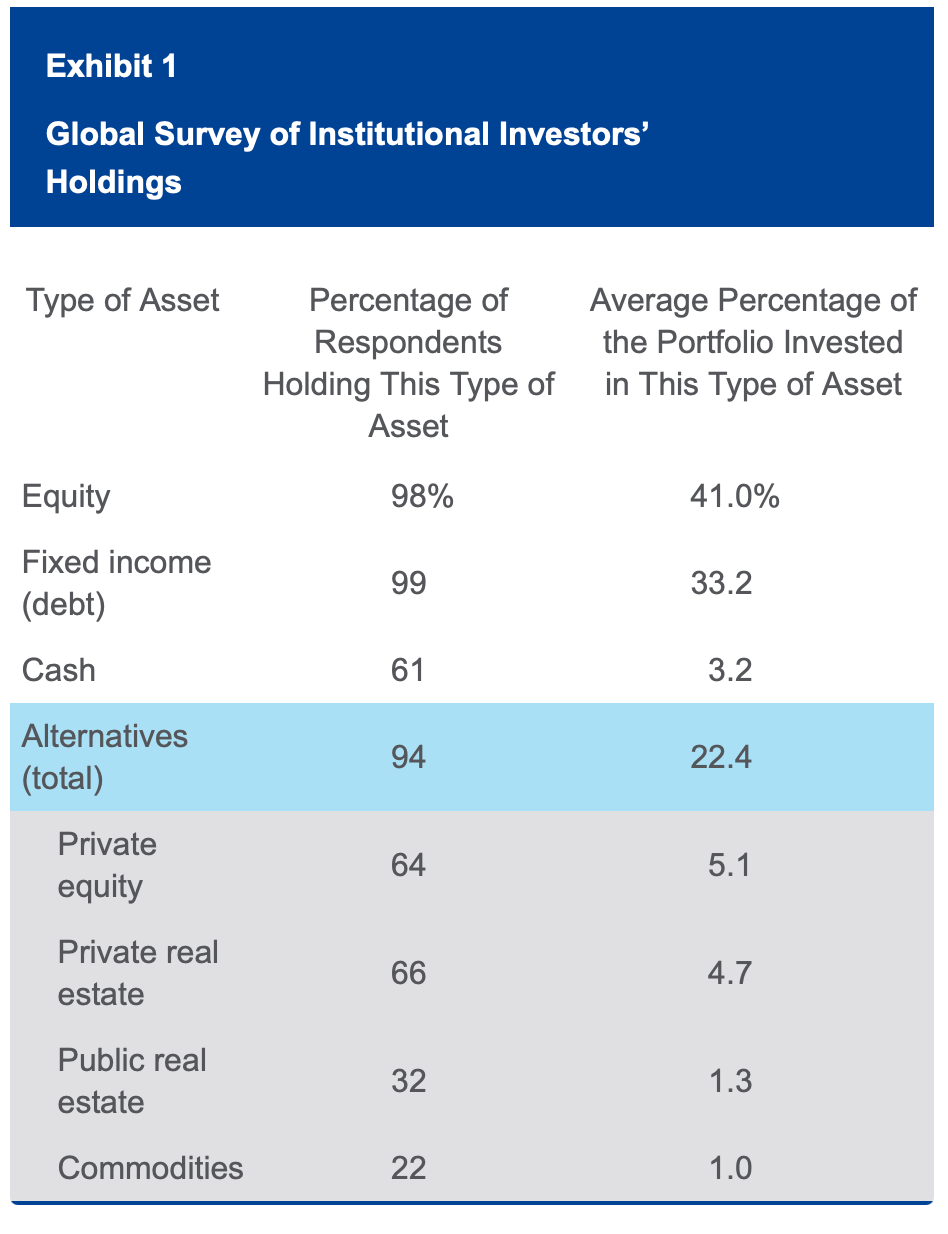
Let’s look at an example of holdings.
As of March 2012, almost 100% of respondents invest in equity and debt. But 94% of them also hold some type of alternative investments. On average, 22.4% of the respondents’ portfolios are invested in alternative investments, with the most popular types being private equity and private real estate.
Limitations:
Although alternative investments have the potential to enhance returns and reduce risk, they also have limitations. Typically, alternative investments are
less regulated and less transparent than traditional investments such as equities and bonds/fixed income (debt).
-Illiquid-hard to sell quick
-Less regulated
-Less transparent
-Liquid
-Difficult to value-typically private companies hard to access how much a startup is worth
-Purchase sale of start-up companies, land or buildings are infrequent so valuation is challenging and based on appraisal, the assessments or estimation of the value of an asset
The benefits of diversification may be reduced in periods of financial crisis when returns on different investments may become more correlated.

Alternative investments are important to balance out your portfolio and not keep all eggs in 1 basket. We all have time, it’s whether we are willing to put in the few hours per month to look into these unique, untraditional but foundational investments that can fuel the most possible growth.